If you’ve been thinking about getting into Bitcoin mining, you’ve come to the right place. Bitcoin (BTC) is the first cryptocurrency, powered by blockchain and distributed ledger technologies. It is designed to facilitate peer-to-peer transactions in an intermediary-free, decentralized environment. Bitcoin mining is the process by which the network validates transactions, adds new blocks, and creates new Bitcoins. It is also known as Bitcoin farming.
In this article, we’ll provide a step-by-step guide on how to mine BTC profitably. We’ll also cover the associated risks and legal implications of Bitcoin mining.
What is Bitcoin Mining?


The Bitcoin blockchain is a decentralized peer-to-peer network that records Bitcoin transactions in unalterable distributed ledgers. BTC mining involves verifying transactions, minting new Bitcoins, and adding new blocks using a proof-of-work (PoW) consensus algorithm.
Miners compete with each other to solve complex mathematical equations, thereby maintaining the security and integrity of the Bitcoin network. The mining process also eliminates double-spending, ensuring nobody can transact the same Bitcoin twice.
To mine Bitcoin, miners use vast amounts of electricity and specialized equipment with immense computational power. The first miner to derive a correct solution can add a proposed block to the blockchain. Successful miners are rewarded with transaction fees and newly created Bitcoins.
As BTC has a fixed supply of 21 million, this reward system will continue only till the last Bitcoin is mined. Afterwards, miners can earn income only from transaction fees.
How Does Bitcoin Mining Work?
The mining process is a network-wide competition among miners to solve cryptographic puzzles. It requires miners to generate a hash equal to or less than the target hash, a 64-digit hexadecimal number set by the network. The difficulty target is adjusted every 2,016 blocks, approximately every two weeks. The greater the number and efficiency of miners in the previous cycle, the higher the mining difficulty.
To generate a winning hash, miners utilize specialized hardware, such as purpose-built application-specific integrated circuits (ASIC) computers. It involves guessing a nonce value and appending it to the hash generated by a mining program.
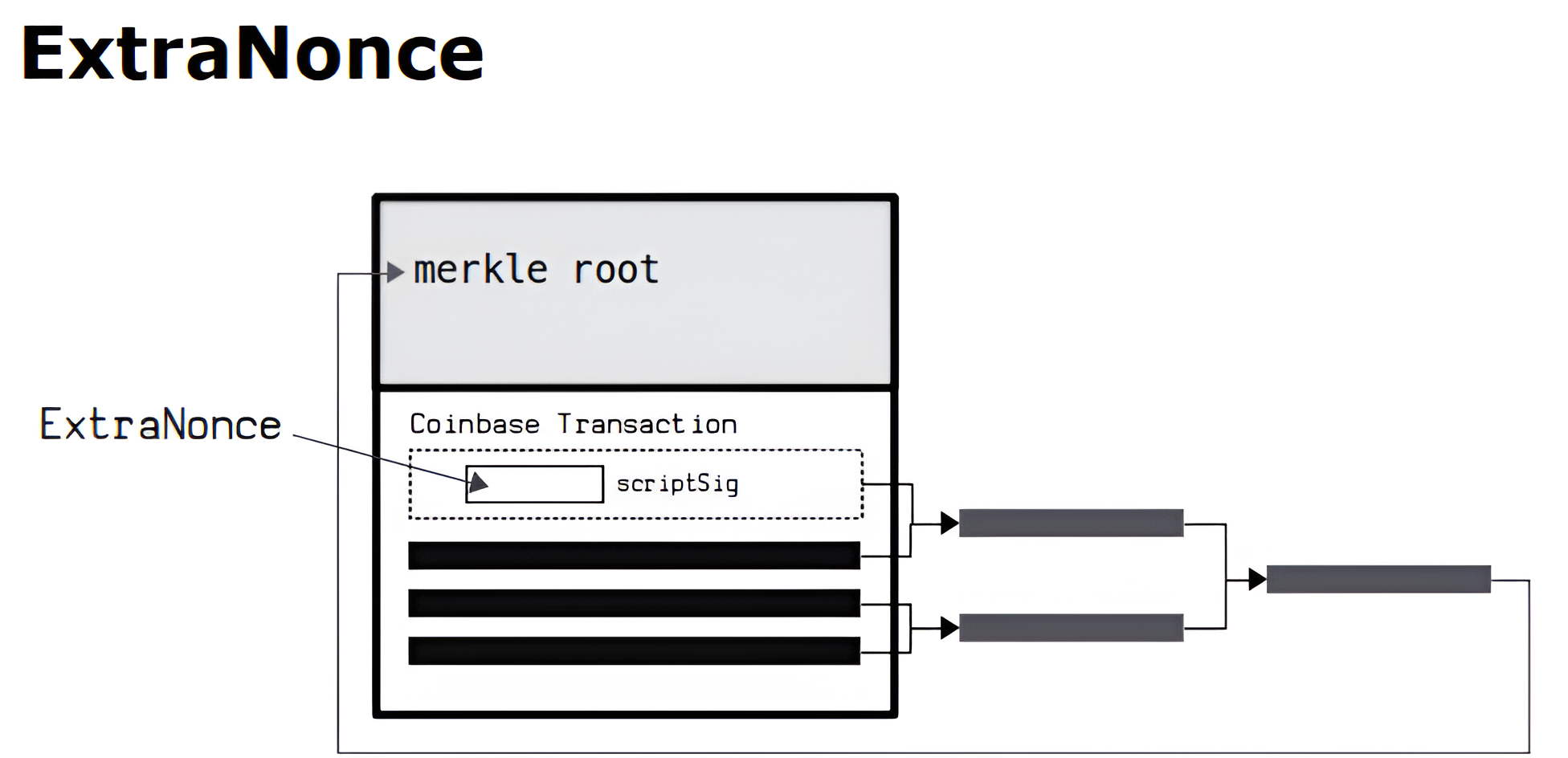

When you commence mining, nonce equals zero. Miners run the block header through a SHA-256 generator to create a hash. If this hash value is greater than the target hash, the attempt is unsuccessful. Miners increment the nonce by 1 for every attempt. However, once the nonce value touches about 4.29 billion, they use another counter called ExtraNonce. It is located inside the Coinbase transaction’s scriptSig.
Miners repeat these steps until they produce a hash and nonce combination that meets the required conditions. The first to successfully reach the specified target adds a new block. The proposed block is broadcast to the network and appended to the blockchain only after other nodes also verify it. The winning miner receives the new Bitcoins and associated fees as block rewards.
Is Bitcoin Mining Still Profitable in 2026?
To make profits, your mining income should exceed the high upfront costs involved. While you can use online profitability calculators, consider the following factors to determine potential returns:
- Mining equipment: You need specialized ASIC machines to mine Bitcoin. Depending on the model you choose, an ASIC computer can cost anywhere between $1,000 – $17,000. Some models, such as the Bitcoin Miner U3S23H, are priced around $35,000. Usually, devices with higher processing power, power efficiency, advanced cooling, and hash rates cost more.
Apart from mining hardware, you need to install power supply units (PSUs), backup generators, reliable internet connections, temperature trackers, and surge protectors. While most mining software applications are free to download, some, like Awesome Miner, are paid.
Additionally, you must incur maintenance costs. Besides, hardware becomes obsolete over time and needs to be replaced periodically.
- Electricity costs: They constitute about 60-80% of total mining costs. Globally, Bitcoin mining operations consume 175 TWh of energy per year, surpassing the annual electricity consumption of countries like Argentina. The amount of electricity required to process a BTC transaction can power a US household for over 49.52 days. Additionally, BTC mining systems generate enormous heat, requiring potent cooling infrastructure to prevent overheating. Therefore, you’ll incur high electricity bills when you mine Bitcoin.
- Block rewards: Mining rewards are halved after every 210,000 BTC are mined, which is approximately every 4 years. The last halving event happened on April 20, 2024, decreasing the reward from 6.25 to 3.125 BTC.
- Bitcoin market price: Bitcoin’s high price volatility makes it challenging to determine whether BTC mining is truly profitable. As of January 20, 2026, Bitcoin is trading at $91,000, a 27.84% decline from its all-time-high of $1,26,080.
- Pool fees: If you join a mining pool, you must incur a fee. The higher the fees, the lower your potential gains.
Methods of Bitcoin Mining
1. ASIC Mining
Due to the rising complexity of Bitcoin mining, ASIC machines have become the go-to choice for most miners. Many models are exclusively designed for the SHA-256 algorithm and perform trillions of calculations per second. They offer high computational power (hash rate), boosting your chances of winning rewards. However, they’re expensive, especially the models with advanced features and sophisticated cooling mechanisms. Examples of popular ASIC machines include MICROBT WhatsMiner M73, Antiminer S21 XP+ Hydro, and Bitdeer SealMiner A3 Pro Hydro.
2. GPU Mining
While GPUs are predominantly used for rendering 3D graphics for video games, they’re capable of performing complex mathematical calculations. They offer more computational power than CPUs and are cheaper than ASIC machines. Therefore, graphics processing units are ideal for solo miners and small-scale mining operations. You can also utilize GPUs to mine multiple digital currencies.
3. CPU Mining
Before Bitcoin gained traction, miners used simple personal computers and central processing units (CPUs) to solve mathematical problems. As the number of participants and Bitcoin’s value surged, mining difficulty increased manifold. Consequently, CPUs could no longer handle advanced calculations. Their slow processing speed, coupled with ever-increasing energy costs, eventually rendered them obsolete for Bitcoin mining.
4. Cloud Mining
Users who lack sufficient funds or don’t wish to purchase specialized hardware can mine BTC through cloud mining platforms. These platforms enable you to rent hashing power from remote data centres. However, you need to pay for the mining contract. Based on the algorithm you want to mine, contract prices will vary.
While cloud mining is a cost-saving method for cryptocurrency mining, it can be a potential scam. Also, most service providers rent resources for specific durations only. Some well-known platforms for Bitcoin mining include Nicehash, ECOS, and Binance.
5. Pool Mining
Mining pools achieve economies of scale by combining the computational power of multiple miners to solve complex mathematical problems. If you join a mining pool, you need to incur only a fraction of the total mining costs. Pool mining also amplifies your winning odds. Whenever a pool successfully mines a block, the rewards are split among participants. Each miner receives rewards proportional to the amount of work and hashing power they contributed. Moreover, the payout per participant is nominal yet consistent.
6. Solo Mining
When individual miners participate in Bitcoin mining using their own resources, it is known as solo mining. As a solo miner, you need significant resources, including specialized equipment and electricity, and must incur mining expenses fully. However, your computing power may be lower than that of mining pools, reducing processing speed and efficiency. Solo mining also requires in-depth technical knowledge and carries higher risks. The only advantage of solo mining is that you earn the entire block reward upon winning.
What Do You Need to Mine Bitcoin?
1. Mining Hardware
You need a powerful ASIC machine purpose-built for Bitcoin’s SHA256 hashing algorithm. Some top ASIC models are Bitmain Antminer S23 Hyd 3U, MicroBT WhatsMiner M79S, and Bitdeer SealMiner A3 Pro Hydro. Additionally, ASIC miners must buy highly-efficient PSUs that provide at least 20% more wattage than their actual energy consumption.
2. Mining Software
You’ll require mining software to connect your hardware to the Bitcoin blockchain. It monitors your hardware’s hash rate and also enables you to receive/send data to the network. Popular mining software such as Kryptex, CGMiner, and BFGMiner are free to download and compatible with ASIC systems. Among paid software, Awesome Miner and Hive OS are worth exploring.
3. Mining Pool
Bitcoin mining pools are groups of miners who combine their processing power and resources to collectively solve tough mathematical problems. They make crypto mining more potentially profitable as they boost the odds of producing a winning hash. Each participant earns rewards proportional to the hashing power they contribute, and incurs lower electricity and hardware costs. Examples of popular mining pools include Foundry, AntPool, F2Pool, and ViaBTC.
4. Additional Requirements
As mining systems generate lots of heat, you need long-lasting cooling and temperature monitoring solutions. You also require an internet connection with low latency, surge protectors, and backup generators to conduct operations despite power outages.
Additionally, you should have a cryptocurrency wallet to participate in BTC mining. A wallet is an encrypted online tool or physical device that enables you to send, receive, and store Bitcoins. Popular Bitcoin wallets include Sparrow, Zengo, and Exodus. Also, it is better to move your Bitcoins into cold wallets like Trezor and Ledger to protect them from online threats.
How to Mine Bitcoin: Step-by-Step Guide
Step 1: Assess Feasibility and Budget
Since Bitcoin mining involves huge upfront investment and maintenance costs, evaluate how much funding and resources you’ve at your disposal. Estimate the amount of money you need to buy/rent additional resources.
Next, study Bitcoin’s historical price trends, crypto market reports, and expert analysis to predict future price movements. Also, mining rewards will be reduced to 1.5625 BTC by 2028. Based on these factors, determine your potential returns to decide whether BTC mining is feasible in the long run.
If you’re planning to set up a Bitcoin farm with cooling systems to store Bitcoin mining hardware, your initial investment will be higher. You also need to evaluate the operational costs for maintaining air conditioners, liquid coolants, and ventilation systems. Therefore, you must do a detailed cost-benefit analysis and estimate vital financial metrics, especially potential ROI.
Step 2: Acquire Necessary Hardware
Given the current difficulty level of Bitcoin mining, you need high-performance ASIC miners with advanced capabilities. They offer greater hash power, making them suitable for large-scale mining. However, they are tailored to specific algorithms, making them less versatile for mining multiple cryptocurrencies. Contrarily, GPUs can handle complex operations but lack the power-efficiency and speed of ASIC devices.
If you’re a serious miner, choose ASIC mining machines. If you’re a solo miner and enjoy mining cryptocurrencies as a hobby, GPUs are worthwhile. Most importantly, assess the durability of devices and the reputation of the manufacturing company before making a purchase.
Step 3: Set Up a Secure Bitcoin Wallet
Whether you want to buy, sell, store, stake, or mine Bitcoin, you need to connect a compatible cryptocurrency wallet. Popular software wallets that are helpful for mining, trading, and preserving BTC are Sparrow, Trust Wallet, Electrum, and Exodus. To ensure your Bitcoins remain safe, move them into cold storage or hardware wallets such as Tangem, Trezor, or Ledger. These wallets store your private keys and seed phrases offline, protecting them from cyber attacks.
Step 4: Join a Mining Pool
As BTC prices are highly volatile, it is hard to forecast whether potential returns will outweigh the expenses you incur. Moreover, solo mining is risky and ineffective if you lack adequate computing power and the ability to manage exorbitant electricity bills. By joining a mining pool, you’ll bear only a portion of the total costs as participants combine their resources. Pools also have a higher likelihood of generating winning hashes and earning rewards.
Step 5: Install and Configure Mining Software
Choose a mining software that is compatible with your specific hardware and seamlessly connects to your mining pool. Based on your preferences and funds at hand, you can download, install, and configure free or paid software. Examples of popular Bitcoin mining software include BFGMiner, EasyMiner, and CGMiner.
Step 6: Start Mining and Monitoring
Once you’ve set up your mining client, follow the instructions provided by your pool to start mining. Monitor your mining activities and regularly assess the condition of your hardware, PSUs, cooling systems, and other resources. Track their energy consumption, temperature, and performance. Update your software and replace obsolete equipment regularly. Lastly, be abreast of the latest events in the crypto world, including changes in cryptocurrency regulations.
How Much Does It Cost to Mine Bitcoin?
1. Mining Machines
If you join a mining pool, you can mine BTC using desktops or gaming computers. However, you’ll receive only nominal rewards based on the amount of work you contributed. Since the incentives are distributed among all participants, your potential earnings are low, especially if you aren’t using ASIC computers.
ASIC systems are potent, enabling you to mine faster and make more money. The best way to improve your chances of earning stable rewards is to buy many ASIC machines and join pools.
For each mining rig, you need to make an upfront investment ranging between $1,000 – $8,000. Some advanced models cost over $34,000. Usually, the higher the efficiency and processing power of a machine, the higher its price.
2. Network Infrastructure
While mining doesn’t require a high-speed internet connection or exceptional bandwidth, it certainly requires low latency. The speed at which your mining shares reach the pool reflects your network’s latency. Moreover, mining farms must install multiple internet connections to ensure each rig is connected to the centralized server/router.
3. Electricity
The mining process requires truckloads of computational power and a 24/7 electricity supply. Mining systems also generate tremendous heat. Therefore, you need air conditioners and sophisticated cooling systems to dissipate heat. Overall, bitcoin mining consumes between 90 – 150 terrawatt-hours of electricity yearly, which is more than the annual consumption of Finland. In essence, miners need to incur substantial electricity costs.
How to Secure Your Mining Rewards?
- Select reputable wallets: Choose well-known crypto wallets with advanced security features like 2FA, insurance fund, and multi-party computation technology to store Bitcoin rewards. If you want trusted third parties to protect your Bitcoins, select custodial wallets. If you desire complete control over your private keys, choose self-custody wallets.
- Back up your private keys and recovery phrases: To safeguard your cryptocurrencies from theft, store your wallet’s private keys and recovery phrases offline. You can store them in airgapped wallets or engrave them on metal plates. You can even split the phrase and preserve each fragment in a different location.
- Avoid public Wi-Fi: Never connect to the internet from public/shared networks, as they’re hot targets for bad actors and hackers. You can also generate a separate guest access on an isolated router, preventing others from accessing your mining resources.
- Download mining software from official websites: Mining software downloaded from unofficial sources could contain viruses and malware that could infect your devices or steal sensitive data.
- Use Secure Shell (SSH) protocol: It is a network protocol that enables you to send data to other computers over unsecured networks. It harnesses cryptography to validate and encrypt connections between multiple devices. It is also helpful for controlling remote servers, executing commands, and transferring files smoothly.
- Secure your device: Ensure you keep your mining software, firmware, and operating systems up-to-date by regularly scanning them for viruses or other online threats.
- Leverage credential management services: If you want to streamline and automate confidential information management, choose services like Hashicorp Vault and Secret Manager. They allow you to store sensitive data, including passwords, user names, SSL certificates, API keys, etc.
- Buy crypto insurance: If you mine/trade cryptocurrencies across multiple blockchains, insure your digital assets against unforeseen events.
- Protect physical infrastructure: Set up access controls and 24/7 surveillance systems to secure your mining infrastructure. Install smart cooling systems and live energy consumption trackers to safeguard your physical infrastructure from permanent damage caused by overheating.
- Join renowned mining pools: Pools may manipulate payouts or close down operations suddenly. Hence, it is essential to choose top mining pools like Poolin, MinerGate, and AntPool.
Challenges and Risks of Bitcoin Mining
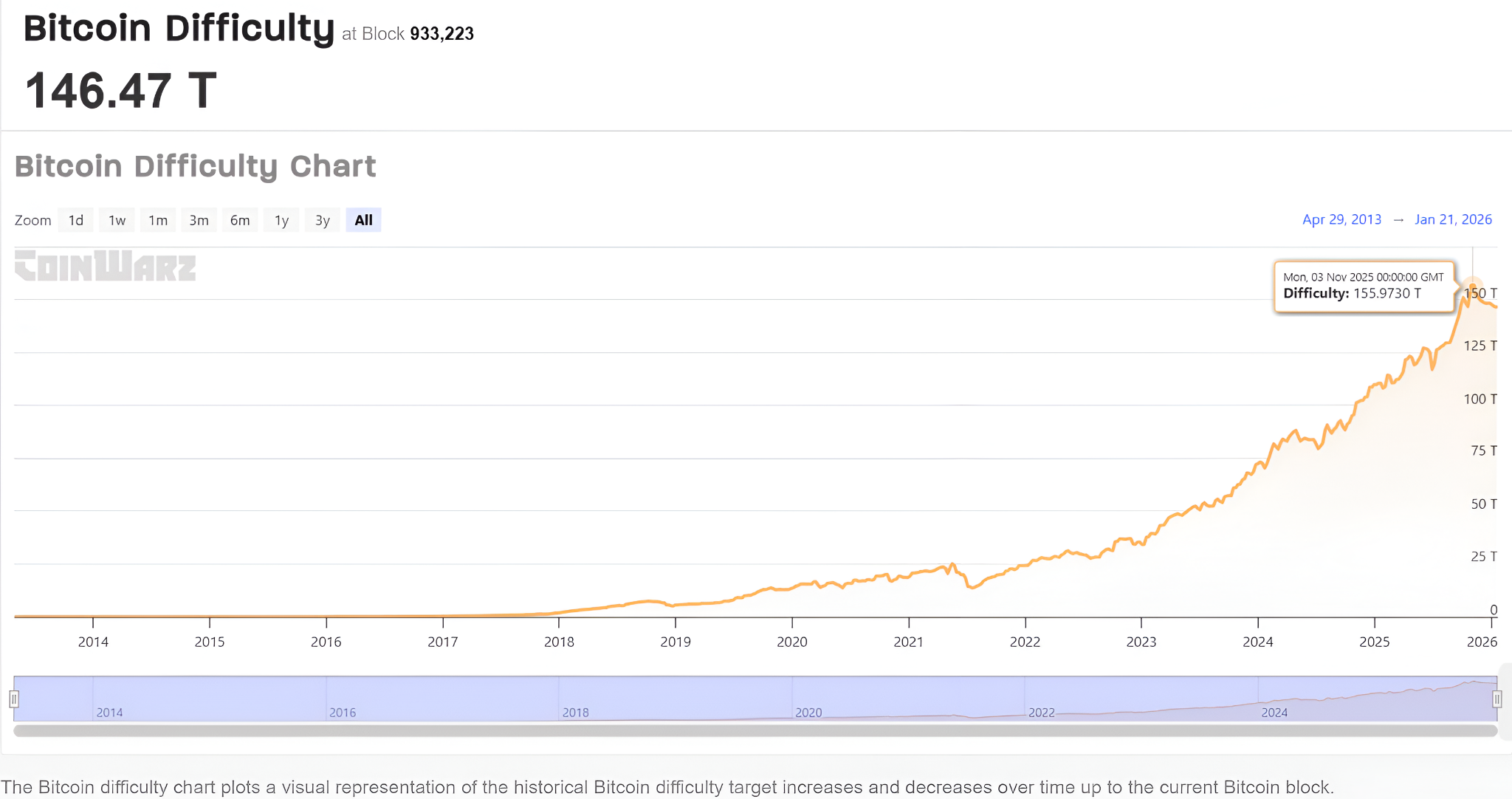

- Difficulty of mining: As Bitcoin is a high-value cryptocurrency, a large number of users participate in the BTC mining process. Many mining farms/pools with highly-efficient ASIC devices have also sprung up, intensifying the competition among Bitcoin miners. In November 2025, the difficulty target touched 155.9730T.
- Significant costs: Mining equipment, including hardware and cooling systems, consumes colossal amounts of energy. The actual mining process that involves decoding PoW puzzles is resource-intensive. If you intend to mine, you need to incur huge upfront costs, especially electricity charges.
- Market volatility: Bitcoin’s price fluctuates rapidly. Hence, it is difficult to precisely forecast your returns from mining.
- Environmental hazards: Bitcoin mining produces significant carbon footprints, greenhouse gas emissions, and electronic waste, impacting the environment adversely.
- Regulatory challenges: Governments are constantly scrutinizing and revising cryptocurrency laws. Moreover, not all countries favor blockchain technology-backed decentralized currencies. They may restrict or ban cryptocurrency mining anytime. Thus, you’re exposed to regulatory risks if you live in locations that aren’t crypto-friendly.
- Scams: From fake wallets, phishing websites, rug pulls, and hacks, the crypto space is a hotbed of scams and fraud. If you aren’t cautious, your confidential credentials may be stolen, leading to a permanent loss of your crypto assets.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations for Bitcoin Mining
There are no uniform cryptocurrency laws or bitcoin mining regulations across the globe. They vary across countries. For example, China has banned BTC mining as it involves heavy energy usage. The US, Canada, and many European countries have embraced cryptocurrencies and support mining activities. El Salvador is the first country to accept Bitcoin as legal tender.
If you want to mine Bitcoin, you must adhere to the laws of your country, including local, zonal, and state-level regulations. Your mining setup shouldn’t breach the energy consumption standards and environmental protocols prescribed in your jurisdiction.
Additionally, mined Bitcoin is treated as taxable income. Moreover, the profits you make from selling BTC are subject to capital gains tax. If you’re running a crypto mining business, you can claim tax exemptions on setup/operational expenses in countries like the US.
Alternatives to Bitcoin Mining
1. Buy and Hold Bitcoin (HODLing)
You can buy Bitcoins on centralized and decentralized exchanges and hold them for a specific period. You can sell them later at a higher price, clocking profits in the process. Many platforms also allow fractional investing, meaning you can purchase a slice of BTC instead of a whole unit.
2. Staking Other Cryptocurrencies
You can stake your idle crypto for fixed or flexible periods to earn passive income. Additionally, you can also use them as collateral to obtain cryptocurrency loans at competitive interest rates. Another option is depositing Bitcoins alongside another cryptocurrency in liquidity mining pools to receive a high annual percentage yield.
3. Joining Cloud Mining Platforms
You can rent mining power from third-party cloud mining service providers. This option is particularly useful for beginners who don’t wish to invest in mining rigs or incur high electricity costs. While you must pay a fee to avail of cloud mining services, you don’t need to worry about setting up or maintaining specialized equipment.
Conclusion
Many miners are gradually gravitating toward renewable energy sources such as hydroelectric, solar, and wind power to reduce carbon emissions. The rise of green mining technologies is further promoting environmentally friendly crypto mining practices. As innovations continue to advance, the Bitcoin mining ecosystem is poised to become more affordable, energy-efficient, and sustainable in the future.
FAQs
To mine 1 Bitcoin or add a block, it takes approximately 10 minutes. The block time also varies based on the difficulty target.
You can mine Bitcoin at home, provided you have the necessary hardware, software, network infrastructure, and computational resources. Since Bitcoin mining is an energy-intensive process, it entails massive upfront costs. Hence, solo mining at home may not be economically viable for all. If you want to earn a stable income or reduce your total outgo, it is worthwhile to join a mining farm/pool.
Whether or not Bitcoin mining is legal depends on your location. Crypto laws, including regulations related to BTC mining, differ from country to country. While some countries like China and Tunisia have prohibited mining, others, such as Ecuador and Morocco, have restricted it. Many nations, like the USA and Canada, support cryptocurrency mining.
Yes. Besides Bitcoin, you can mine other cryptocurrencies like Litecoin, Dogecoin, Monero, and Ravencoin. In general, blockchain networks that follow the proof-of-work consensus mechanism involve crypto mining.
No. You can’t mine Bitcoin for free. Whether you’re an individual miner or a pool member, you’ve to incur mining costs entirely or partially. If you opt for cloud mining services, you’ve to pay a fee for renting hash power. However, many of these platforms offer trial periods, task-based rewards, free hash power credits, limited-time bonuses, and referral rewards. They enable you to experiment with Bitcoin mining for a temporary period at zero cost.